
What is Apprenticeship?
An apprenticeship is a structured program that combines practical, hands-on work experience with formal education and training. It is designed to help individuals develop the skills, knowledge, and competencies required for a specific trade, profession, or career path. Apprenticeships are often available to individuals of various ages and educational backgrounds, making them a flexible option for career development or a pathway to switch industries. The Apprenticeship Act, 1961 is an Indian law that provides the framework for the regulation and promotion of apprenticeship training in the country. The Apprenticeship Act, 1961, has been amended several times to align with changing industrial needs. This Act has been instrumental in creating a skilled workforce for India’s industrial and economic development.
Key Features of an Apprenticeship:
On-the-Job Training:
Apprentices work under the guidance of experienced professionals to gain practical skills in a real-world environment.
Earn While You Learn:
Apprenticeships often provide a salary or stipend, allowing participants to earn money while acquiring skills.
Certification:
Upon completion, apprentices receive a certification or qualification that demonstrates their expertise, which is often nationally or internationally recognized.
Mentorship:
Apprentices benefit from close mentorship by industry professionals, which helps them navigate the challenges of the trade.
Establishment Eligibility:
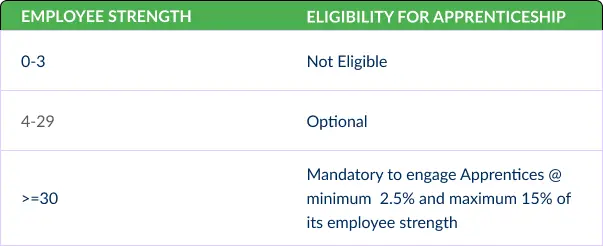
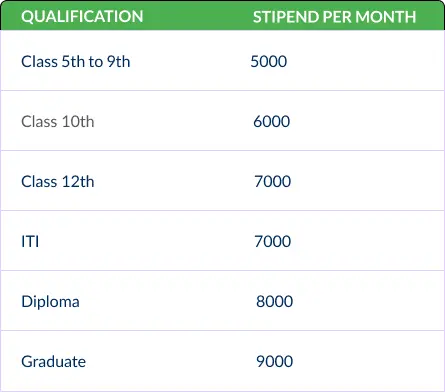
Minimum Prescribed Stipend:

National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)
NAPS stands for the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme; a program launched by the Government of India under Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship on 2016 to promote apprenticeship training, incentivize employers to engage apprentices by sharing stipend costs and increase the engagement of employers in creating skilled workers. It is part of the government’s broader initiative to enhance employability and skill development in line with the Skill India Mission.
Objectives of NAPS:
Encourage Employers:
To incentivize employers to hire apprentices by sharing a portion of the stipend cost.
Increase Apprenticeship Opportunities:
To make apprenticeship a mainstream training model across industries.
Bridge the Skill Gap:
To align workforce skills with the needs of the industry and improve job readiness.
Empower Youth:
Enhances workforce productivity and reduces skill gaps.
Apprentices Eligibility:
Minimum eligibility of 14 years for Non-Hazardous Industries and 18 years for Hazardous Industries.
Maximum age limits up to 35 years
Educational qualification from class 5th to Graduate
Establishments Benefits:
Exemption of Labor Laws
Utilization of CSR Funds
Financial support of 25% of minimum prescribed stipend or 1500 per month per apprentice for a duration of 1 year
Providing PF/ESI and Minimum wages is not mandatory
Apprentices Benefits:
Earn while learning through a structured stipend.
Gain industry-relevant skills and practical experience.
Improved employability and career prospects.

National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS)
NATS stands for the National Apprenticeship Training Scheme, was implemented in 1968 by the Government of India under the Apprenticeship Act, 1961. It is designed to provide technical graduates and diploma holders with practical training in their respective fields, bridging the gap between formal education and the demands of the workforce. Financial support under the National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS) began in 2016 as part of the Indian government's initiative to incentivize both students and employers to participate in apprenticeship training. This was a significant step towards making the scheme more attractive and impactful, aligning with the broader Skill India Mission.
Objectives of NATS:
Skill Enhancement:
To improve the employability of graduates and diploma holders by providing hands-on training.
Industry Readiness:
To ensure that individuals entering the workforce are equipped with practical skills aligned with industry requirements.
Public-Private Partnership:
To encourage collaboration between educational institutions, industries, and the government.
Apprentices Eligibility:
Diploma and Graduates
Should be within 5 years of completion at the time of registration
Establishments Benefits:
Exemption of Labor Laws
Utilization of CSR Funds
Financial support of 50% of minimum prescribed stipend per month per apprentice for a duration of 1 year
Providing PF/ESI and Minimum wages is not mandatory
Apprentices Benefits:
Gain industry-specific skills and practical experience.
Receive financial support during the training period.
Improve employability and career prospects.
Download reference materials here

Get a Free Consultation
+91 9901920043



